Identify the sixth phase of the systems life cycle – The sixth phase of the systems life cycle, encompassing implementation, post-implementation evaluation, maintenance, and evolution, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the success and longevity of any information system. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of this crucial phase, exploring its significance, key activities, and best practices.
Understanding the sixth phase empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and maximize the value derived from their technology investments. By embracing a holistic approach to systems implementation and management, organizations can harness the full potential of their information systems and drive business growth.
Sixth Phase of Systems Life Cycle

The sixth phase of the systems life cycle, implementation, is crucial for transitioning the designed system into a fully functional reality. This phase involves deploying the system into the production environment, ensuring its seamless integration with existing systems and business processes.
Key Activities and Tasks
- Hardware and software installation
- Data conversion and migration
- System testing and acceptance
- User training and documentation
- System launch and deployment
Implementation Considerations
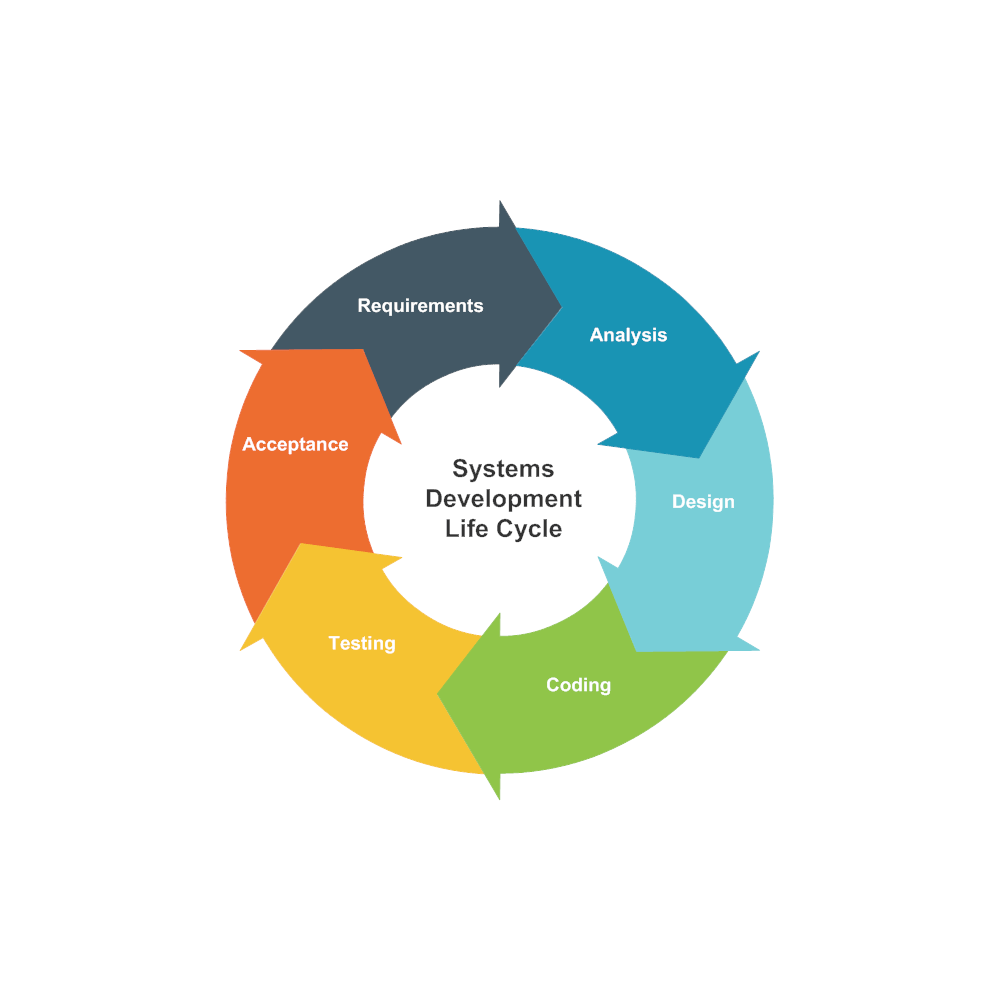
Factors to Consider
- Technical feasibility and compatibility
- Resource availability (hardware, software, personnel)
- Business impact and disruption
- User acceptance and training
- Legal and regulatory compliance
Challenges and Risks
- Technical failures or incompatibilities
- Inadequate user training or resistance
- Unforeseen business disruptions
- Cost overruns or delays
Best Practices
- Thorough planning and preparation
- Phased implementation to minimize disruption
- Comprehensive user training and support
- Contingency plans for potential risks
- Regular monitoring and evaluation
Post-Implementation Evaluation: Identify The Sixth Phase Of The Systems Life Cycle
Importance of Evaluation
Post-implementation evaluation is critical for assessing the effectiveness and success of the newly implemented system. It provides valuable insights into areas for improvement and ensures alignment with business objectives.
Metrics and Methods
- System usage and adoption rates
- Efficiency and productivity improvements
- Error rates and system reliability
- User satisfaction and feedback
- Return on investment (ROI)
Case Studies
Case studies showcase real-world examples of successful post-implementation evaluations, highlighting the benefits and lessons learned.
Maintenance and Evolution
Ongoing Activities, Identify the sixth phase of the systems life cycle
- Bug fixes and system updates
- Performance monitoring and optimization
- User support and training
- Compliance and regulatory updates
- System enhancements and upgrades
Identifying and Addressing Issues
Effective maintenance involves proactively identifying and addressing system issues through regular monitoring, user feedback, and issue tracking.
Keeping the System Up-to-Date
Regular updates and enhancements are crucial for maintaining system functionality, security, and alignment with evolving business needs.
FAQ
What is the purpose of the sixth phase of the systems life cycle?
The sixth phase, encompassing implementation, post-implementation evaluation, maintenance, and evolution, ensures the successful deployment, operation, and ongoing optimization of the information system.
What are the key activities performed during the sixth phase?
Key activities include system deployment, user training, performance monitoring, issue resolution, and ongoing system enhancements to meet evolving business needs.
How can organizations mitigate risks associated with systems implementation?
Risk mitigation strategies include thorough planning, stakeholder engagement, robust testing, and contingency plans to address potential challenges.